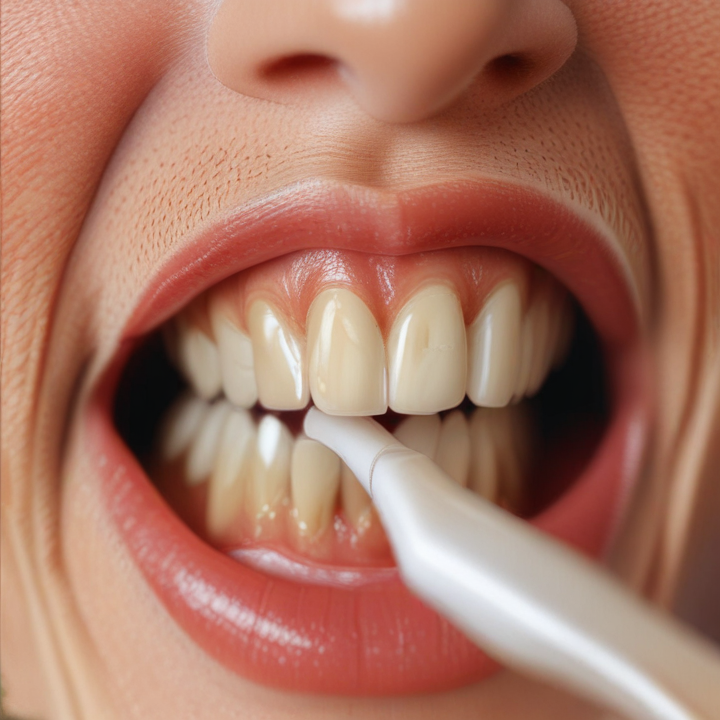
escaner intraoral Safety Certifications
Intraoral scanners, used extensively in dental practices, must adhere to strict safety certifications to ensure they are safe for both patients and practitioners. Key certifications and standards include:
1. ISO 13485: This international standard specifies requirements for a quality management system where an organization needs to demonstrate its ability to provide medical devices and related services that consistently meet customer and applicable regulatory requirements.
2. IEC 60601-1: This standard addresses the general requirements for basic safety and essential performance of medical electrical equipment. Intraoral scanners must comply with these standards to ensure they do not pose electrical hazards.
3. FDA Clearance: In the United States, intraoral scanners must receive clearance from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This involves a rigorous review process to ensure the device is safe and effective for its intended use.
4. CE Marking: For the European market, intraoral scanners must have the CE mark, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
5. RoHS Compliance: The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive ensures that intraoral scanners do not contain harmful substances like lead, mercury, or cadmium, which can pose risks to health and the environment.
6. IEC 62304: This standard specifies life cycle requirements for the development of medical software, ensuring that the software used in intraoral scanners is designed with safety in mind.
7. ISO 10993: This series of standards evaluates the biocompatibility of medical devices to manage any potential biological risks to patients.
By adhering to these standards and obtaining these certifications, manufacturers of intraoral scanners demonstrate their commitment to safety and quality, ensuring that their devices are reliable and safe for clinical use.
List Reference Technical Parameters of "escaner intraoral"
Intraoral scanners (IOS) are essential tools in modern digital dentistry, offering high precision and ease of use. Here are the key technical parameters and features of intraoral scanners:
1. Accuracy (Trueness and Precision): Accuracy is a crucial parameter, often divided into trueness (how close the scan is to the actual object) and precision (the consistency of the scan results). Intraoral scanners generally provide accuracy within a clinically acceptable margin of error, often around 0.05 mm.
2. Scanning Speed: The speed of scanning impacts the efficiency of the workflow. Modern intraoral scanners are designed to capture images quickly, often within minutes, reducing the time patients need to stay still and improving overall clinic throughput.
3. Ergonomics: The design of the scanner, including its weight and the size of the handpiece, is optimized for ease of use. Lightweight models, often around 130-350 grams, are common, and ergonomic designs minimize strain on the operator's wrist.
4. Color Accuracy: High-quality intraoral scanners produce realistic color images, which are crucial for diagnostics and treatment planning. Scanners that offer vivid, true-to-life color imaging allow for better visualization of dental structures and conditions.
5. Autoclavable Tips: For infection control, many scanners feature autoclavable tips, ensuring that they can be sterilized between uses without degradation.
6. Connectivity and File Formats: Intraoral scanners often support open file formats like STL and PLY, which are compatible with a variety of CAD software. This flexibility allows for seamless integration into different digital workflows.
7. Special Features: Many scanners come with additional features such as automatic fog prevention, plug-and-play capability for easy sharing between workstations, and options for implantology or orthodontic applications.
8. Software and Licenses: Some scanners come with software licenses that offer lifetime use without additional fees, while others might require annual fees. The presence of integrated software can enhance functionality, offering features like real-time visualization and enhanced diagnostic tools.
These parameters ensure that intraoral scanners provide high-quality, efficient, and reliable digital impressions, which are essential for modern dental practices.
List Product features of "escaner intraoral"
An intraoral scanner is a device used in dentistry to create a digital impression of a patient's oral cavity. Here are some key features of an intraoral scanner:
1. High-Resolution Imaging: Provides detailed 3D images of the teeth and gums, ensuring accurate digital impressions.
2. Speed and Efficiency: Quickly captures the entire oral structure, reducing the time needed for traditional impression methods.
3. Ergonomic Design: Compact and lightweight for easy handling and patient comfort.
4. Real-Time Scanning: Displays images in real-time on a connected screen, allowing for immediate assessment and adjustments.
5. Digital Integration: Easily integrates with CAD/CAM systems for seamless digital workflows in restorative and orthodontic procedures.
6. Wireless Capability: Some models offer wireless functionality for increased mobility and ease of use in the dental clinic.
7. Color Scanning: Captures images in full color, helping in better visualization and differentiation of oral tissues.
8. Open Architecture: Compatible with various software and systems, providing flexibility in choosing dental lab partners and solutions.
9. Ease of Use: Intuitive interface and user-friendly software make it accessible for dental professionals of all experience levels.
10. Patient Comfort: Non-invasive scanning method enhances patient experience compared to traditional impression materials.
11. Accurate Measurements: Delivers precise measurements crucial for fitting crowns, bridges, and aligners.
12. Data Storage: Securely stores patient data and digital impressions for future reference and treatment planning.
13. Infection Control: Designed with sterilizable or disposable scanner tips to maintain high hygiene standards.
14. Cloud Connectivity: Some models feature cloud-based data storage and sharing options, facilitating collaboration and remote consultations.
15. Artificial Intelligence: Advanced AI features assist in detecting dental issues and suggesting treatment options.
These features collectively enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and patient experience in modern dental practices.
List Various Types of "escaner intraoral"
Intraoral scanners are advanced dental tools used to capture detailed digital impressions of a patient’s mouth. They are pivotal in modern dentistry for procedures such as orthodontics, prosthodontics, and implantology. Here are several types of intraoral scanners:
1. iTero Element: Produced by Align Technology, the iTero Element series offers high precision and is known for its integration with Invisalign, making it a popular choice for orthodontic treatments.
2. Trios: Developed by 3Shape, the Trios series is recognized for its speed and accuracy. It includes features like shade measurement and HD photos, enhancing the diagnostic capabilities.
3. CEREC Primescan: From Dentsply Sirona, Primescan offers excellent accuracy and speed. It's highly regarded for its ease of use and seamless integration with CEREC software for chairside CAD/CAM restorations.
4. Medit i500/i700: Medit’s i500 and i700 models are known for their affordability and user-friendly software. These scanners are lightweight and offer high-quality images, making them suitable for a variety of dental applications.
5. Carestream CS 3600/3700: These scanners from Carestream Dental provide high-resolution 3D images and are appreciated for their ergonomic design and ease of use. They also offer flexible workflow options.
6. Planmeca Emerald: Planmeca’s Emerald scanners are compact and deliver precise digital impressions. They are praised for their lightweight design and integration with Planmeca’s comprehensive software suite.
7. 3M True Definition: Known for its affordability and precision, the 3M True Definition scanner offers high accuracy and an open architecture system that is compatible with various CAD/CAM systems.
8. Heron IOS: The Heron Intraoral Scanner by 3DISC provides high-quality scanning with a lightweight and ergonomic design. It is designed to be cost-effective without compromising on performance.
9. Vatech EZScan: Vatech’s EZScan is appreciated for its intuitive user interface and high precision. It is a reliable option for capturing detailed dental impressions.
These scanners vary in features, cost, and compatibility with different software systems, allowing dental professionals to choose the best fit for their practice needs.
List Application of "escaner intraoral"
Intraoral scanners are advanced devices used in dentistry to capture detailed 3D images of the inside of a patient's mouth. These digital impressions have various applications, including:
1. Prosthodontics: Intraoral scanners facilitate the design and fabrication of dental prostheses such as crowns, bridges, and veneers. The precise digital impressions ensure better fitting restorations and reduce the need for adjustments.
2. Orthodontics: These scanners are used to create accurate digital models for orthodontic planning and treatment, including the design of braces and clear aligners like Invisalign. This leads to more accurate treatment plans and improved patient outcomes.
3. Implantology: Intraoral scanners aid in planning and placing dental implants. They provide detailed images of the oral cavity, allowing for precise implant positioning and custom abutments, enhancing the overall success of implant procedures.
4. Restorative Dentistry: They are used to capture accurate data for restorative procedures such as fillings and inlays/onlays. The digital impressions help in creating restorations that match the patient's natural teeth perfectly.
5. Cosmetic Dentistry: Intraoral scanners assist in planning and executing cosmetic procedures by providing high-resolution images that guide the design of aesthetically pleasing restorations, ensuring a natural look.
6. Patient Education and Communication: The detailed images from intraoral scanners can be used to educate patients about their dental conditions and proposed treatments, enhancing understanding and communication between the dentist and patient.
7. Digital Workflow Integration: These scanners streamline the dental workflow by integrating with CAD/CAM systems, enabling the seamless design and manufacturing of dental restorations, reducing the turnaround time and improving efficiency.
8. Record Keeping and Monitoring: Intraoral scanners create digital records of a patient’s oral condition, which can be used for monitoring changes over time, making it easier to track progress and detect issues early.
Overall, intraoral scanners significantly improve the precision, efficiency, and patient experience in various dental procedures.
List Buyer Types of "escaner intraoral"
Buyers of intraoral scanners, such as the "escaner intraoral," typically fall into several distinct categories:
1. General Dentists: These professionals use intraoral scanners for a variety of applications including crowns, bridges, dentures, and night guards. They value scanners for their ability to improve accuracy and efficiency, reducing the time needed for impressions and enhancing patient satisfaction with quicker, more comfortable procedures.
2. Orthodontists: Intraoral scanners are essential for orthodontists, particularly those who work with clear aligner systems like Invisalign. The high accuracy and speed of these scanners help in creating precise aligner trays and other orthodontic appliances, improving treatment outcomes and patient experiences.
3. Prosthodontists: Specialists in prosthodontics use intraoral scanners to design and create dental prostheses. The detailed digital impressions provided by these scanners are crucial for fabricating high-quality crowns, bridges, and implants, ensuring a better fit and function for patients.
4. Dental Laboratories: These buyers utilize intraoral scanners to receive digital impressions from dentists, which they then use to manufacture dental restorations and appliances. The digital workflow streamlines communication between the lab and dental offices, reducing turnaround times and enhancing the precision of the final products.
5. Educational Institutions: Dental schools and training centers invest in intraoral scanners to educate future dental professionals on the latest technology in digital dentistry. These institutions need reliable and user-friendly scanners that can demonstrate the full range of digital dental procedures.
6. Mobile Dental Services: Providers offering mobile dental services, especially in underserved areas, use portable intraoral scanners to perform on-site dental diagnostics and treatments. The portability and ease of use of modern scanners are crucial for these applications.
7. Patients: Although not direct buyers, patients increasingly prefer dentists who use advanced technology like intraoral scanners. These devices improve the overall patient experience by making procedures quicker, more accurate, and less invasive.
Intraoral scanners are valued across these buyer types for their ability to enhance clinical decision-making, improve workflow efficiency, and increase patient engagement and satisfaction.
List "escaner intraoral" Project Types for Different Industries
Intraoral scanners are revolutionizing various industries beyond their primary use in dentistry. Here are some project types for different industries:
1. Dentistry and Orthodontics:
- Digital Impressions: Capture high-precision images of patients' teeth for accurate diagnoses and treatment planning.
- Orthodontic Treatment Planning: Create 3D models for designing braces and aligners.
- Prosthodontics: Design crowns, bridges, and dentures with high precision.
2. Medical Research and Development:
- Biometric Studies: Collect detailed oral cavity data for research on dental diseases and conditions.
- Prosthetic Development: Innovate new dental prosthetics and materials using precise digital models.
3. Education and Training:
- Dental School Training: Provide hands-on experience with digital impression techniques for students.
- Virtual Simulations: Develop realistic simulations for training in diagnosis and treatment planning.
4. Manufacturing:
- Custom Dental Products: Create customized dental products such as mouthguards and retainers.
- Quality Control: Implement high-precision quality checks for dental products.
5. Technology and Software Development:
- CAD/CAM Systems: Integrate intraoral scanners with computer-aided design and manufacturing systems for streamlined workflows.
- Software Development: Create advanced software solutions for processing and analyzing digital impressions.
6. Healthcare Marketing:
- Patient Education: Develop interactive tools and apps to educate patients on dental procedures using 3D scans.
- Marketing Campaigns: Utilize high-quality images for marketing dental services and products.
7. Insurance and Claims:
- Claims Processing: Use detailed digital scans to support dental insurance claims and reduce fraud.
8. Telehealth:
- Remote Consultations: Enable remote dental consultations using digital impressions for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Intraoral scanners are versatile tools that extend far beyond traditional dentistry, impacting various sectors with their precision and digital capabilities.
escaner intraoral Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Intraoral scanners, essential for modern dental practices, come with a variety of accessories and upgrades that enhance their functionality and user experience. Custom manufacturing options further tailor these devices to specific clinical needs.
Accessories:
1. Tips and Sleeves: Disposable and autoclavable tips ensure hygiene and ease of use. Various sizes and shapes cater to different scanning requirements.
2. Calibration Tools: Regular calibration ensures accuracy. These tools are essential for maintaining the scanner’s precision.
3. Charging Stations: Docking and charging stations streamline the use of wireless scanners, providing convenient storage and quick recharging.
4. Mounting Solutions: Articulating arms and stands allow for flexible positioning, making scanning more comfortable for both the practitioner and patient.
5. Protective Cases: Durable cases protect scanners during transport, crucial for practices with multiple locations or those providing mobile services.
Upgrades:
1. Software Enhancements: Upgrading software can introduce new features such as AI-driven analysis, enhanced image quality, and faster processing times.
2. Connectivity Options: Enhanced connectivity features, including wireless options and cloud integration, streamline workflow and data management.
3. Battery Upgrades: Extended battery life ensures that wireless scanners can operate for longer periods without interruption.
4. Resolution Improvements: Hardware upgrades can improve image resolution, providing more detailed scans and better diagnostic capabilities.
Custom Manufacturing Options:
1. Ergonomic Customization: Custom grips and handles can be manufactured to fit the practitioner’s hand size and preference, improving comfort and reducing fatigue.
2. Specialized Tips: Custom tips designed for specific dental procedures or patient demographics (e.g., pediatric patients) can enhance scanning efficiency.
3. Color and Branding: Custom colors and branding options help practices maintain a professional and cohesive look.
4. Enhanced Durability: Custom builds using more robust materials can extend the lifespan of the scanner, especially in high-usage environments.
These accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options ensure that intraoral scanners can meet the evolving needs of dental professionals, enhancing both functionality and patient care.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "escaner intraoral"
Quality Control in Intraoral Scanner Manufacturing
Design and Development:
1. Prototyping: Initial designs are created and tested for functionality.
2. Software Integration: Ensuring software correctly captures and processes 3D images.
3. User Feedback: Prototypes are tested by dental professionals for usability insights.
Component Quality:
1. Material Selection: High-quality, biocompatible materials are chosen.
2. Supplier Verification: Components are sourced from verified suppliers to ensure consistency.
Manufacturing Process:
1. Precision Manufacturing: Using CNC machines and 3D printers to create accurate components.
2. Assembly: Assembled in cleanroom environments to prevent contamination.
3. Calibration: Each unit is calibrated to ensure accuracy in capturing intraoral images.
Testing and Validation:
1. Functional Testing: Each scanner is tested to ensure it meets performance specifications.
2. Durability Testing: Units are subjected to stress tests to verify durability.
3. Software Validation: Ensuring the scanner’s software integrates seamlessly with dental practice management systems.
Regulatory Compliance:
1. Certifications: Compliance with international standards like ISO 13485 and FDA regulations.
2. Documentation: Thorough documentation for traceability and compliance verification.
Post-Production Quality Control:
1. Final Inspection: Each unit undergoes a final inspection before packaging.
2. Random Sampling: Regular random sampling of units to ensure ongoing quality.
3. Customer Feedback: Gathering and analyzing customer feedback for continuous improvement.
The Manufacturing Process of Intraoral Scanners
1. Conceptualization and Design:
- Initial concept development based on market needs.
- Detailed design using CAD software.
2. Prototyping:
- Creating prototypes using 3D printing and other rapid prototyping techniques.
- Iterative testing and refinement.
3. Component Manufacturing:
- Precision manufacturing of optical components, electronics, and housing.
- Use of high-quality, biocompatible materials.
4. Assembly:
- Manual and automated assembly processes in cleanroom environments.
- Integration of optical, electronic, and mechanical components.
5. Calibration and Testing:
- Calibration of optical systems for accuracy.
- Comprehensive testing of hardware and software.
6. Quality Assurance:
- Final inspection and functional testing of each unit.
- Adherence to ISO and FDA standards.
7. Packaging and Shipping:
- Secure packaging to protect during transit.
- Distribution to global markets.
This streamlined approach ensures high-quality, reliable intraoral scanners ready for dental applications.
How to use "escaner intraoral"
Using an intraoral scanner involves several steps to ensure accurate digital impressions of a patient's mouth. Here’s a concise guide:
1. Preparation:
- Ensure the scanner and computer are properly set up and connected.
- Confirm the patient’s mouth is clean and dry. Use air or gauze to dry the teeth and gums.
2. Patient Positioning:
- Seat the patient comfortably with good lighting.
- Position the patient’s head so you can access all areas of the mouth easily.
3. Scanner Calibration:
- Turn on the scanner and follow the manufacturer's instructions for calibration.
- Ensure the scanner tip is clean and properly attached.
4. Scanning Procedure:
- Begin with the upper or lower arch. Start from one quadrant, typically the molars.
- Gently insert the scanner into the patient’s mouth. Ensure the tip is positioned correctly.
- Move the scanner slowly and steadily across the teeth. Maintain a consistent distance from the teeth to capture accurate images.
- Cover all areas, including occlusal, buccal, and lingual surfaces. Pay attention to detail, ensuring no areas are missed.
- For full-arch scans, proceed to the adjacent quadrant and repeat the process.
5. Real-Time Feedback:
- Most intraoral scanners provide real-time feedback. Monitor the screen for areas that need rescanning.
- Adjust angles and re-scan areas if the software indicates incomplete or inaccurate data.
6. Finalizing the Scan:
- Once all quadrants are scanned, review the digital model on the screen.
- Use the software tools to trim and refine the scan if necessary.
- Ensure the scan captures the entire dental arch and occlusion accurately.
7. Saving and Sending:
- Save the scan data according to the software instructions.
- Send the digital impressions to the lab or relevant software for further processing.
8. Post-Scan Care:
- Clean the scanner tip thoroughly.
- Store the scanner in a safe place to avoid damage.
Following these steps ensures high-quality digital impressions and optimal use of the intraoral scanner.
"escaner intraoral" Comparative Analysis
Intraoral scanners (IOS) have revolutionized dental practices by offering a digital alternative to traditional impression methods. Here's a comparative analysis of some leading intraoral scanners:
1. TRIOS by 3Shape
- Accuracy and Speed: Known for high precision and fast scanning speeds, the TRIOS series offers real-time visualizations and a user-friendly interface.
- Software Integration: Excellent integration with CAD/CAM systems and numerous dental practice management software.
- Cost: Higher price point, reflecting its advanced technology and capabilities.
2. iTero by Align Technology
- Accuracy and Speed: Offers reliable accuracy, especially valued for orthodontic applications like Invisalign. Scanning speed is competitive but can be slower than TRIOS in some settings.
- Software Integration: Seamless integration with Invisalign and other orthodontic tools. Good overall integration with other dental software.
- Cost: Moderately priced, often chosen for its specific alignment with orthodontic treatments.
3. CEREC Primescan by Dentsply Sirona
- Accuracy and Speed: One of the highest accuracy rates, especially for complex restorative procedures. Fast scanning speeds and easy-to-use interface.
- Software Integration: Strong integration with CEREC CAD/CAM systems, making it ideal for same-day restorations.
- Cost: Premium pricing, justifiable by its advanced features and integration capabilities.
4. Medit i500
- Accuracy and Speed: Offers good accuracy and speed, though not as high as TRIOS or Primescan. However, it provides a reliable performance for general dental practices.
- Software Integration: Decent integration with major dental software, but not as seamless as some premium brands.
- Cost: More affordable, providing a cost-effective option for practices seeking a balance between price and performance.
5. Planmeca Emerald S
- Accuracy and Speed: High accuracy with improved scanning speed compared to its predecessor. Particularly noted for its ergonomic design.
- Software Integration: Integrates well with Planmeca’s suite of products and other major dental software.
- Cost: Mid-range pricing, offering good value for its features.
Conclusion
Choosing the right intraoral scanner depends on specific practice needs, budget, and desired integration with existing systems. TRIOS and CEREC Primescan lead in accuracy and advanced features, while iTero is preferred for orthodontics. Medit i500 and Planmeca Emerald S offer cost-effective alternatives with reliable performance.
"escaner intraoral" Warranty and Support
When investing in an intraoral scanner, understanding the warranty and support options is crucial for ensuring long-term value and reliability. Here's a summary of key aspects typically offered:
Warranty
1. Duration: Most manufacturers provide a standard warranty period ranging from one to three years. Extended warranties can often be purchased to cover additional years.
2. Coverage: The warranty usually covers defects in materials and workmanship. This typically includes repairs or replacements of faulty components without additional costs.
3. Exclusions: Be aware that the warranty might not cover damage caused by misuse, accidents, unauthorized modifications, or normal wear and tear.
4. Process: In case of a defect, the process often involves contacting customer support, diagnosing the issue, and either sending the device in for repair or receiving a replacement.
Support
1. Technical Support: Manufacturers offer technical support through various channels such as phone, email, and online chat. This support can help with troubleshooting, software updates, and usage guidance.
2. Training: Comprehensive training is usually provided to ensure users can maximize the device's capabilities. This can include in-person training sessions, online webinars, and access to training materials.
3. Software Updates: Continuous software updates are essential for maintaining the scanner’s performance and compatibility with other dental software. Many manufacturers provide these updates free of charge during the warranty period.
4. Maintenance Plans: Some companies offer maintenance plans that include regular check-ups and servicing to prevent potential issues. These plans can also extend support beyond the warranty period.
Additional Considerations
- Response Time: Check the average response and resolution times for support inquiries.
- User Community: Some manufacturers host forums or user groups for sharing experiences and solutions.
- Local Support: Verify if local support centers or certified service providers are available in your area for quicker assistance.
Overall, thoroughly reviewing the warranty and support terms before purchasing an intraoral scanner will ensure you are well-prepared to handle any technical issues and maintain optimal functionality.
List "escaner intraoral" FAQ
Escáner Intraoral FAQ
1. ¿Qué es un escáner intraoral?
Un escáner intraoral es un dispositivo digital que captura imágenes en 3D del interior de la boca, incluyendo dientes y encías, para facilitar diagnósticos y tratamientos dentales.
2. ¿Cómo funciona un escáner intraoral?
El escáner utiliza una cámara pequeña que se mueve por la boca del paciente, capturando imágenes detalladas que luego se combinan para crear un modelo 3D preciso.
3. ¿Cuáles son las ventajas de usar un escáner intraoral?
- Precisión: Genera modelos altamente detallados.
- Comodidad: Es menos invasivo que los moldes tradicionales.
- Rapidez: Reduce el tiempo de consulta y mejora la eficiencia en los tratamientos.
- Digitalización: Facilita el almacenamiento y envío de información.
4. ¿Para qué tratamientos se utiliza un escáner intraoral?
- Ortodoncia (alineadores transparentes, brackets)
- Implantes dentales
- Coronas y puentes
- Evaluación de caries y desgaste dental
5. ¿Es seguro el uso de un escáner intraoral?
Sí, es seguro. No utiliza radiación y es una herramienta no invasiva.
6. ¿Qué preparación se necesita antes de usar un escáner intraoral?
No se requiere preparación especial. Es recomendable que el paciente tenga la boca limpia.
7. ¿Cuánto tiempo tarda un escaneo intraoral?
Dependiendo del caso, puede tardar entre 5 y 15 minutos.
8. ¿Puede cualquier dentista utilizar un escáner intraoral?
Los dentistas necesitan capacitación específica para manejar correctamente el dispositivo y interpretar los resultados.
9. ¿Cuáles son las limitaciones de un escáner intraoral?
- Algunas áreas de la boca pueden ser difíciles de escanear.
- No puede sustituir todas las pruebas radiológicas.
10. ¿Cómo se comparan los escáneres intraorales con los métodos tradicionales?
Los escáneres son más cómodos y precisos que los moldes de silicona tradicionales, además de proporcionar resultados digitales inmediatos.