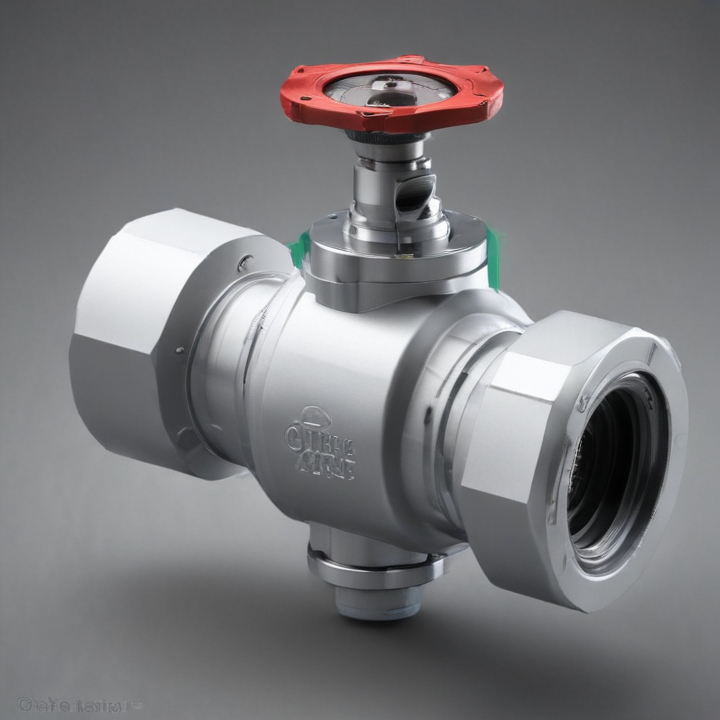
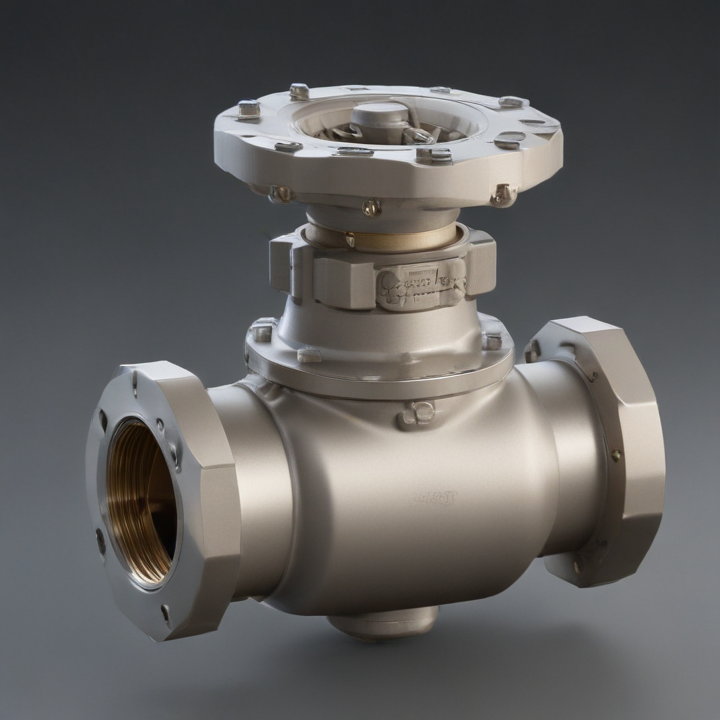
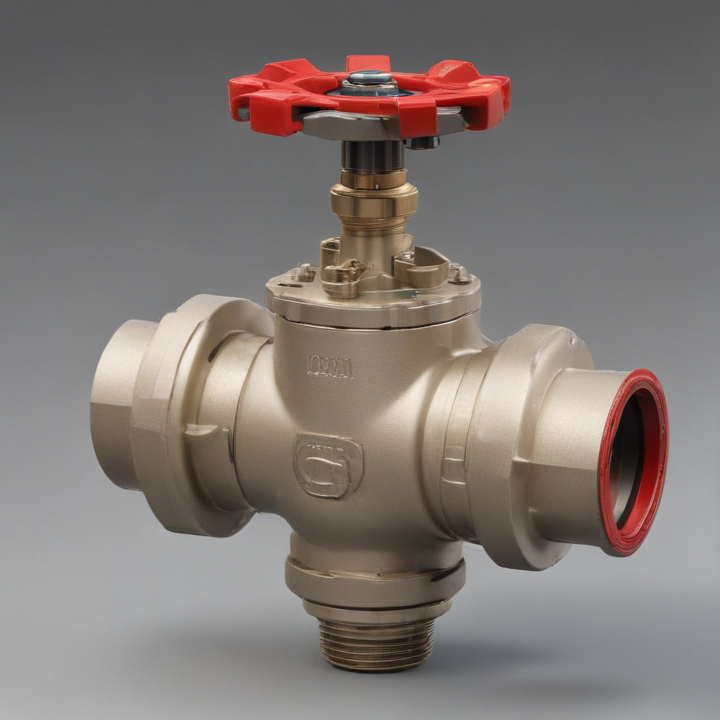
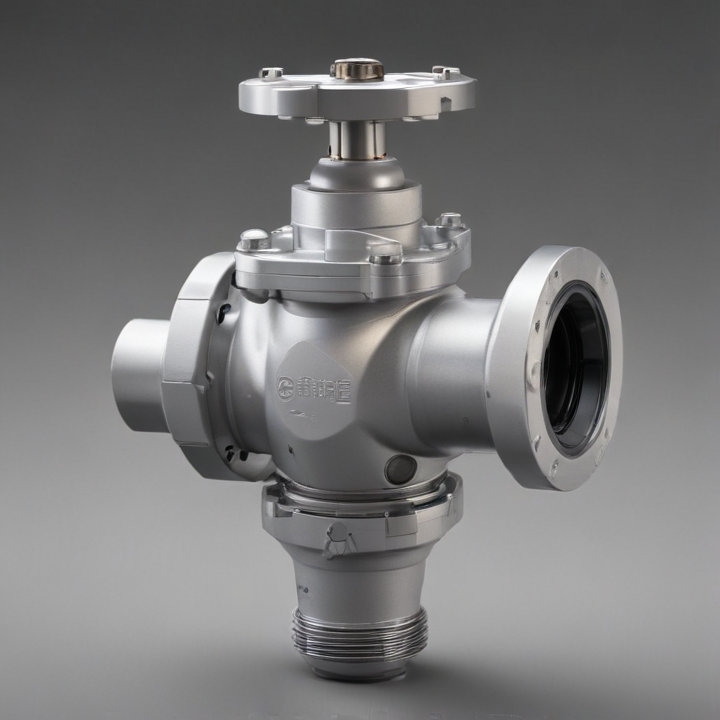
orbit valve Safety Certifications
Orbit valves, known for their high integrity and long service life, adhere to several critical safety certifications and standards, ensuring their reliability and performance in demanding applications.
1. ISO 15848 and API 622 Certifications: Orbit valves are certified to ISO 15848 Tightness Class AH and API Standard 622. These standards are crucial for valves used in applications with strict emission controls, guaranteeing low fugitive emissions even under extreme temperatures and dynamic cycling conditions.
2. ASME and National Board Certifications: Valve manufacturers, including those producing Orbit valves, typically comply with the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Codes (BPVC). They obtain ASME Certification Marks such as V (Power boilers safety valves), HV (Heating boilers safety valves), NV (Nuclear installation and shop assembly), UV (Pressure vessels safety valves), and UD (Pressure vessels rupture discs). Additionally, National Board certifications like the R, VR, and NR stamps are essential for repair and maintenance services, indicating adherence to stringent safety and quality standards.
3. TÜV Functional Safety Certification: Some Orbit valve products, particularly those designed for critical safety shut-off applications, are certified by TÜV for functional safety. This certification ensures compliance with international safety standards like IEC 61508 and IEC 61511, which are essential for maintaining operational safety and integrity in various industrial environments.
These certifications demonstrate Orbit valves' commitment to meeting and exceeding industry safety standards, making them a reliable choice for critical applications across various sectors.
List Reference Technical Parameters of "orbit valve"
Reference Technical Parameters of Orbit Valve
Design and Construction:
- Valve Type: Ball valve (or quarter-turn valve)
- Body Material: Often available in carbon steel, stainless steel, and special alloys
- End Connections: Flanged, welded, or threaded connections
- Pressure Rating: ANSI Class 150 to Class 2500 (varies with specific design)
- Size Range: Typically from 1/2 inch to 42 inches
- Temperature Range: -50°F to 1000°F (depending on material and application)
Operational Features:
- Actuation: Manual, electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuators
- Sealing Mechanism: Metal-to-metal seat or soft seat options
- Stem Design: Blowout-proof stem for safety
- Operation: Quarter-turn operation for quick opening and closing
- Leakage Class: Zero leakage (ANSI/FCI 70-2 Class VI for soft seated, Class V for metal seated)
Performance Specifications:
- Flow Characteristics: Equal percentage or linear flow control
- Torque Requirements: Variable, depending on size and pressure conditions
- Cycle Life: High cycle life, typically over 100,000 cycles
- Cv (Flow Coefficient): Specific to valve size and pressure rating
Compliance and Standards:
- Standards Compliance: API 6D, ASME B16.34, ISO 9001, NACE MR0175/ISO 15156
- Fire Safety: API 607, API 6FA
- Emissions: Low emissions, compliant with ISO 15848-1
Additional Features:
- Inspection and Testing: 100% tested for pressure, leakage, and operational performance
- Maintenance: Designed for ease of maintenance with replaceable components
- Corrosion Protection: Options for internal and external coatings for enhanced durability
- Availability of Configurations: Wide range of configurations including side entry, top entry, and fully welded designs
These parameters ensure that orbit valves are reliable, durable, and suitable for a wide range of demanding applications in industries such as oil and gas, petrochemical, and power generation.
List Product features of "orbit valve"
An "orbit valve" is a specialized type of valve commonly used in the oil and gas industry, known for its unique design and specific features that enhance its performance and reliability. Below are the key features of an orbit valve:
1. Cam-Driven Mechanism: Orbit valves utilize a unique cam-driven mechanism that lifts the seal from the seat before rotating, reducing wear and extending the valve's lifespan.
2. Zero Leakage: The valve is designed to ensure zero leakage, even in high-pressure and high-temperature environments, providing reliable sealing performance.
3. Non-Rubbing Rotation: The non-rubbing rotation of the valve mechanism eliminates friction between sealing surfaces, preventing galling and ensuring smooth operation.
4. Durable Sealing: With a robust sealing system, orbit valves can handle severe service conditions, including those with abrasive or corrosive media.
5. High-Pressure Capability: These valves are capable of handling high-pressure applications, making them suitable for critical service conditions in the oil and gas industry.
6. Bi-Directional Flow: Orbit valves allow for bi-directional flow, providing flexibility in installation and operation.
7. Low Maintenance: The design minimizes wear and tear, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and ensuring long-term reliability.
8. Fire-Safe Design: Many orbit valves are designed to be fire-safe, complying with industry standards to ensure safety in hazardous environments.
9. Metal-to-Metal Sealing: The metal-to-metal sealing system ensures high integrity and reliability in sealing performance, even under extreme conditions.
10. Compact Design: The compact design of orbit valves makes them suitable for applications with space constraints.
11. Wide Temperature Range: They can operate effectively across a wide range of temperatures, enhancing their versatility in various industrial applications.
12. High Flow Capacity: The design allows for high flow capacity, ensuring efficient fluid handling in large-scale operations.
13. Low Operating Torque: The efficient design ensures low operating torque, making the valve easier to operate and reducing the need for large actuators.
These features make orbit valves a preferred choice for critical applications requiring reliable, leak-proof, and maintenance-friendly solutions.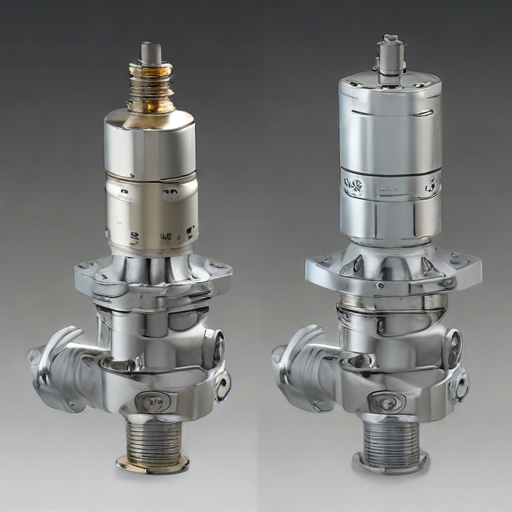
List Various Types of "orbit valve"
Orbit valves are specialized ball valves designed for high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosive applications, often used in the oil and gas industry. Here are various types of orbit valves:
1. Top-Entry Orbit Valve: This type allows maintenance and inspection without removing the valve from the pipeline, facilitating easy access to internal components.
2. Side-Entry Orbit Valve: Typically split-body designs, side-entry valves are assembled from the side. They are easier to manufacture and maintain compared to top-entry valves.
3. Metal-Seated Orbit Valve: Designed for high-temperature and abrasive conditions, these valves use metal seats instead of soft materials to ensure durability and performance under harsh conditions.
4. Soft-Seated Orbit Valve: These valves use softer materials like PTFE for the seat, offering a better seal in less demanding applications and providing bubble-tight shutoff.
5. Manual Orbit Valve: Operated manually using a handwheel or lever, suitable for applications where automated control is not necessary.
6. Pneumatic Actuated Orbit Valve: Uses pneumatic actuators for automated operation, ideal for remote or hazardous environments where manual operation is impractical.
7. Electric Actuated Orbit Valve: Equipped with electric actuators for precise control, these valves are often used in applications requiring automation and remote control.
8. Cryogenic Orbit Valve: Specifically designed for extremely low temperatures, these valves are used in applications involving liquefied gases like LNG.
9. Subsea Orbit Valve: Engineered for underwater applications, typically featuring robust construction and materials resistant to seawater corrosion and high pressures.
10. High-Pressure Orbit Valve: Designed to withstand very high pressures, these valves are used in critical applications such as wellheads and choke and kill lines.
11. Trunnion-Mounted Orbit Valve: The ball in these valves is supported by trunnions, reducing the torque required to operate the valve and making them suitable for high-pressure applications.
Each type of orbit valve is tailored for specific operating conditions, offering various advantages depending on the requirements of the application.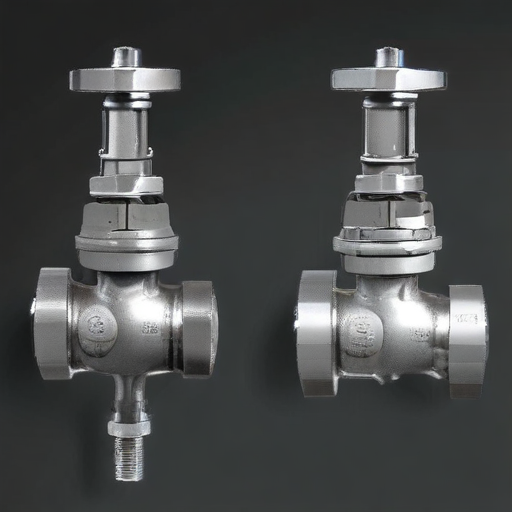
List Application of "orbit valve"
Orbit valves, known for their robust design and precise operation, are primarily used in various industrial applications due to their unique quarter-turn mechanism, which ensures a reliable seal and minimal wear and tear. Key applications include:
1. Oil and Gas Industry: Orbit valves are extensively used in upstream, midstream, and downstream sectors. They handle crude oil, natural gas, and refined products, ensuring safe and efficient flow control in pipelines, processing facilities, and storage terminals.
2. Petrochemical Industry: These valves manage the flow of various chemicals and petrochemicals in processing plants. Their durability and leak-proof sealing are crucial for handling hazardous and corrosive substances.
3. Power Generation: In power plants, orbit valves regulate steam and water flow in high-pressure and high-temperature environments, contributing to the efficiency and safety of operations.
4. Refineries: Orbit valves are used to control the flow of hydrocarbons and other fluids in refining processes. Their ability to maintain a tight seal even under high pressure and temperature is vital for operational reliability.
5. Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Plants: These valves are essential in LNG processing and transportation, where they manage cryogenic temperatures and prevent leakage of highly volatile substances.
6. Pipelines: Orbit valves provide reliable isolation and flow control in long-distance pipelines, ensuring minimal maintenance and operational downtime.
7. Chemical Plants: These valves handle various chemical substances, offering corrosion resistance and precise control necessary for safe and efficient plant operation.
8. Water Treatment Facilities: Orbit valves are employed in controlling the flow of water and other fluids in treatment processes, providing durability and reliable performance.
9. Mining Industry: In mining operations, orbit valves are used to manage the flow of slurries and abrasive materials, offering robustness against harsh conditions.
10. Pharmaceutical Industry: Orbit valves ensure clean and precise flow control of various liquids and gases used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Orbit valves’ versatility and reliability make them integral to critical flow control applications across numerous industries.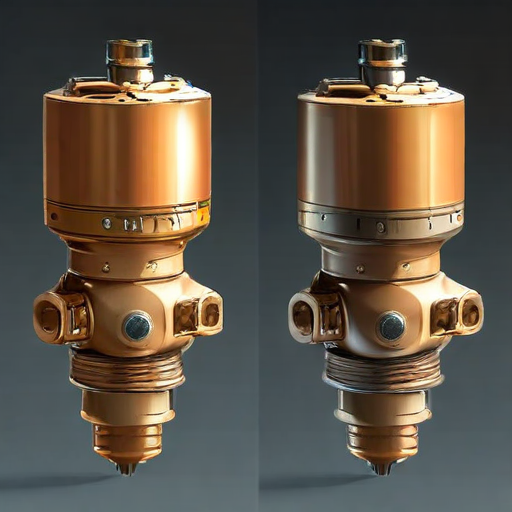
List Buyer Types of "orbit valve"
"Orbit valve" buyers can be categorized into several distinct types based on their specific needs, industries, and applications. Here are the primary buyer types:
1. Oil and Gas Industry:
- Exploration and Production Companies: These buyers use orbit valves for drilling and extraction processes, ensuring the safe and efficient flow of oil and gas.
- Refineries and Petrochemical Plants: They require orbit valves for various processes, including crude oil distillation, cracking, and refining.
- Pipeline Operators: Companies that manage the transportation of oil and gas use orbit valves to control the flow and pressure within pipelines.
2. Chemical Industry:
- Chemical Processing Plants: These facilities need orbit valves to manage the flow of chemicals during production, ensuring precise control and safety.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturers: These buyers use orbit valves in processes that require stringent controls to maintain purity and prevent contamination.
3. Power Generation:
- Nuclear Power Plants: Orbit valves are critical in managing the flow of cooling fluids and other essential processes within nuclear reactors.
- Thermal Power Plants: These facilities use orbit valves to control steam and other fluids in power generation processes.
4. Water and Wastewater Management:
- Municipal Water Treatment Facilities: Orbit valves help manage the flow and treatment of water and wastewater, ensuring clean water supply and proper waste disposal.
- Industrial Wastewater Treatment: Industries that produce significant wastewater require orbit valves for effective treatment and disposal.
5. Aerospace and Defense:
- Aerospace Manufacturers: They use orbit valves in various fluid control systems within aircraft and spacecraft.
- Defense Contractors: These buyers need orbit valves for military applications, including submarines and other naval vessels.
6. Food and Beverage Industry:
- Food Processing Plants: These facilities use orbit valves to manage the flow of ingredients and products during processing, ensuring hygiene and precision.
- Beverage Manufacturers: Similar to food processing, beverage manufacturers require orbit valves for controlled and sanitary fluid handling.
7. General Industrial Applications:
- Manufacturing Plants: Various industries use orbit valves in their production lines to manage fluids and gases.
- HVAC Systems: Companies involved in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning use orbit valves to control the flow of air and refrigerants.
Each of these buyer types seeks orbit valves for their reliability, precision, and ability to handle critical applications across diverse environments.
List "orbit valve" Project Types for Different Industries
Orbit valves are essential components in various industries, offering reliable performance and safety. Here are some project types for different industries utilizing orbit valves:
1. Oil and Gas Industry:
- Upstream Projects: Exploration and production facilities often require orbit valves for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
- Midstream Projects: Transportation and storage facilities, such as pipelines and storage tanks, utilize orbit valves for flow control and isolation.
- Downstream Projects: Refineries and petrochemical plants need orbit valves for handling corrosive and abrasive fluids.
2. Chemical Industry:
- Production Plants: Chemical manufacturing processes use orbit valves for precise control of various chemicals.
- Processing Units: Orbit valves are essential in units like distillation columns, reactors, and separators, ensuring safe and efficient operations.
3. Power Generation:
- Thermal Power Plants: Orbit valves are used in steam and cooling water circuits to manage high-pressure steam and other fluids.
- Nuclear Power Plants: Critical applications involving radioactive fluids require the robust design and reliability of orbit valves.
4. Water and Wastewater Treatment:
- Desalination Plants: Orbit valves help manage high-salinity water and brine, ensuring reliable operation in corrosive environments.
- Municipal Treatment Facilities: Used in various stages of water purification and wastewater treatment processes.
5. Mining Industry:
- Processing Plants: Orbit valves are used in the processing of minerals and ores, particularly in slurry and abrasive material handling.
- Tailings Management: Ensuring the safe and efficient handling of mining by-products.
6. Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Manufacturing Facilities: Precise control of clean and sterile fluids is crucial, and orbit valves provide the necessary reliability and hygiene.
7. Food and Beverage Industry:
- Processing Plants: Orbit valves are used for handling various food-grade fluids, ensuring compliance with hygiene standards.
These project types demonstrate the versatility and critical importance of orbit valves across multiple industries, ensuring safe, efficient, and reliable operations in diverse applications.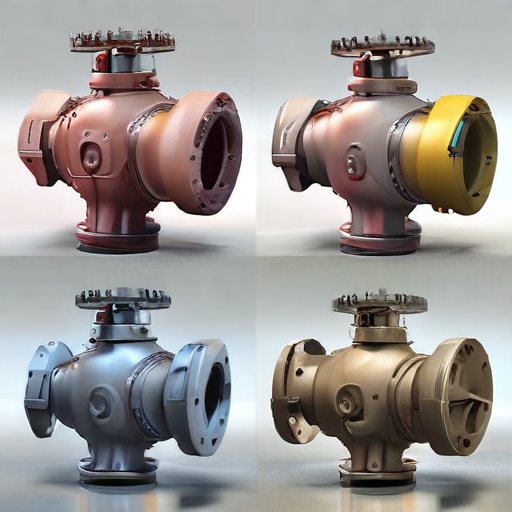
orbit valve Accessories Upgrades and Custom Manufacturing Options
Orbit Valve offers a range of accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options to enhance the functionality and performance of their valves. These enhancements are designed to meet the specific needs of various industrial applications, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Accessories:
1. Actuators: Available in both manual and automated options, including pneumatic, hydraulic, and electric actuators for precise control.
2. Positioners: Enhance control accuracy by providing feedback on valve position.
3. Limit Switches: Enable remote monitoring of valve position to ensure operational safety.
4. Solenoid Valves: For quick and efficient control of valve operation in automated systems.
5. Gear Operators: Facilitate manual operation of large or high-pressure valves with ease.
Upgrades:
1. Advanced Sealing Systems: Offer improved leak resistance and durability in harsh environments.
2. Corrosion-Resistant Coatings: Extend valve life in corrosive applications.
3. High-Temperature Materials: Enable valves to operate effectively in extreme temperature conditions.
4. Pressure Relief Features: Enhance safety by preventing over-pressurization.
5. Extended Stem Options: Allow for easier operation in buried or hard-to-reach installations.
Custom Manufacturing Options:
1. Material Selection: Customizable valve bodies and components in a variety of materials, including stainless steel, alloy steels, and exotic metals for specific application requirements.
2. Size and Pressure Ratings: Custom valves can be manufactured to meet unique size and pressure specifications.
3. Special Coatings and Linings: Tailored to resist specific chemicals or environmental conditions.
4. Customized End Connections: Including flanged, welded, or threaded ends to fit existing piping systems.
5. Tailored Flow Characteristics: Custom-designed trim and internals to achieve desired flow rates and characteristics.
By offering these accessories, upgrades, and custom manufacturing options, Orbit Valve ensures that its products can be precisely tailored to meet the diverse needs of their customers, enhancing performance, reliability, and longevity.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of "orbit valve"
Quality Control in the Manufacturing Process of Orbit Valve
1. Raw Material Inspection
- Material Verification: Ensure materials meet specified standards.
- Chemical Composition Analysis: Verify materials' chemical properties.
2. Machining and Manufacturing
- CNC Machining: Precision cutting using CNC machines.
- Dimensional Inspection: Measure components using calipers, micrometers, and CMMs.
- Surface Finish Check: Inspect surface roughness and finish quality.
3. Assembly Process
- Component Fitment: Check for proper fit and alignment of components.
- Torque Testing: Ensure bolts and fasteners are tightened to specified torque values.
4. Pressure Testing
- Hydrostatic Testing: Test valves under high-pressure water to check for leaks and structural integrity.
- Pneumatic Testing: Use air or gas for leak detection under specified pressure conditions.
5. Functional Testing
- Operational Testing: Cycle the valve open and closed to ensure smooth operation.
- Seal Integrity: Check for proper sealing without leaks.
6. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
- Ultrasonic Testing: Detect internal flaws using high-frequency sound waves.
- Radiographic Testing: Use X-rays to identify internal defects.
7. Final Inspection
- Visual Inspection: Check for surface defects, proper markings, and overall appearance.
- Documentation Review: Verify all quality control documents and test reports.
8. Packaging and Shipping
- Protective Packaging: Ensure valves are packaged to prevent damage during transit.
- Labeling: Clearly label with specifications, testing results, and certification.
9. Continuous Improvement
- Feedback Loop: Use customer feedback and internal audits to continually improve processes.
- Training: Regularly train staff on the latest quality control techniques and standards.
By implementing rigorous quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process, Orbit Valve ensures its products meet the highest standards of reliability and performance.
How to use "orbit valve"
An "Orbit valve" is a type of valve known for its unique quarter-turn design, commonly used in industrial applications to control the flow of liquids and gases. Here’s a concise guide on how to use an Orbit valve:
Steps to Use an Orbit Valve
1. Installation:
- Positioning: Ensure the valve is installed in the correct orientation as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. The flow direction should align with the arrow marked on the valve body.
- Connection: Securely connect the valve to the piping system using appropriate flanges or threaded connections. Ensure all connections are tight to prevent leaks.
2. Operation:
- Opening the Valve:
- Turn the valve handle or actuator 90 degrees counterclockwise. The handle should align with the pipeline when open.
- For actuated valves, ensure the actuator is properly powered and follow the actuator’s operating instructions.
- Closing the Valve:
- Turn the handle or actuator 90 degrees clockwise. The handle should be perpendicular to the pipeline when closed.
3. Maintenance:
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the valve for any signs of wear, corrosion, or leakage.
- Lubrication: Lubricate the valve components as recommended by the manufacturer to ensure smooth operation.
- Cleaning: Clean the valve and its surroundings to prevent debris from affecting its performance.
4. Safety:
- Pressure Checks: Ensure the system is depressurized before performing any maintenance.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE such as gloves and safety goggles when handling the valve.
5. Troubleshooting:
- If the valve fails to operate, check for blockages, ensure the actuator (if present) is functioning correctly, and verify that there is no internal damage.
By following these steps, you can effectively use an Orbit valve to control flow in your industrial system. Regular maintenance and proper operation are key to ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
"orbit valve" Comparative Analysis
Orbit Valve Comparative Analysis
1. Design and Construction:
Orbit valves are known for their unique, non-rubbing rotational design, minimizing wear and tear and ensuring longer operational life. Traditional ball or gate valves often suffer from sealing surface wear due to their sliding action. The Orbit valve’s design eliminates this issue by employing a camming mechanism that lifts the core away from the seat before rotating, thus reducing friction and wear.
2. Sealing Mechanism:
The sealing mechanism in Orbit valves is robust, ensuring tight shutoff even in severe service conditions. The valve's seat remains protected from the flow, which reduces erosion and enhances sealing performance over time. This is a significant advantage over conventional valves, where the sealing surfaces are continuously exposed to the flow, leading to potential leaks.
3. Application Suitability:
Orbit valves are particularly suited for applications requiring zero leakage and high reliability, such as in the oil and gas industry, chemical plants, and power generation. Their design makes them ideal for handling corrosive, abrasive, or high-temperature fluids. In contrast, conventional valves may require frequent maintenance or replacement in these harsh environments.
4. Maintenance and Operational Cost:
Orbit valves generally offer lower maintenance requirements and extended service intervals due to their minimal wear design. This can translate to lower operational costs over the valve’s lifecycle. Traditional valves might require more frequent servicing, leading to higher maintenance costs and potential downtime.
5. Operational Safety:
The non-rubbing design of Orbit valves significantly reduces the risk of operational failures, enhancing safety in critical applications. This is especially important in industries where valve failure could lead to hazardous situations. Conventional valves, with their higher wear rates, might pose a greater risk of operational failure.
6. Economic Considerations:
While Orbit valves tend to have a higher upfront cost compared to standard ball or gate valves, the total cost of ownership can be lower due to their durability, reduced maintenance needs, and longer service life. This makes them a cost-effective choice in the long run for demanding applications.
Conclusion:
Orbit valves offer distinct advantages over traditional valve designs in terms of durability, reliability, and operational efficiency. Their unique construction and sealing mechanisms make them particularly valuable in harsh environments where valve performance is critical.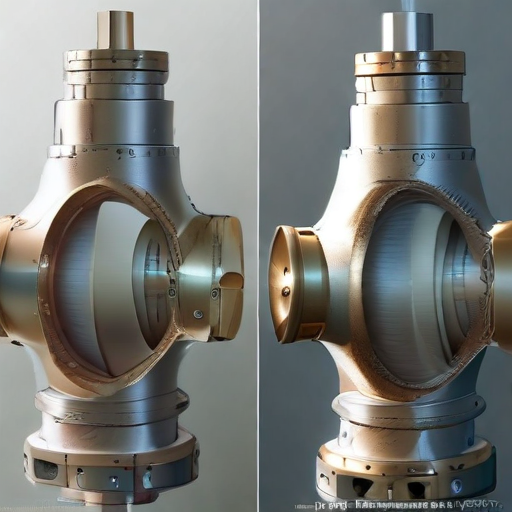
"orbit valve" Warranty and Support
Orbit Valve Warranty and Support
Warranty Information:
Orbit Valve offers a comprehensive warranty to ensure the reliability and durability of their products. Typically, their valves come with a standard limited warranty, covering defects in materials and workmanship for a specified period, often ranging from one to five years depending on the product type. The warranty is effective from the date of purchase and requires proof of purchase for validation.
Key Warranty Terms:
1. Coverage: The warranty covers the repair or replacement of defective valves under normal use and maintenance.
2. Exclusions: Damages resulting from misuse, improper installation, unauthorized modifications, and external factors such as corrosion due to environmental conditions are not covered.
3. Claim Process: To initiate a warranty claim, customers should contact Orbit Valve's customer service, providing the product details, proof of purchase, and a description of the issue. The company may require the defective product to be returned for inspection.
Support Services:
Orbit Valve is committed to providing exceptional support to ensure customer satisfaction and optimal valve performance.
Technical Support:
- Installation Guidance: Detailed installation manuals and video tutorials are available to assist customers in proper installation and setup.
- Troubleshooting Assistance: Customers can access troubleshooting guides on the company’s website or contact the technical support team via phone or email for personalized help.
Customer Service:
- Product Inquiries: For questions regarding product features, compatibility, and specifications, the customer service team is readily available.
- Maintenance Tips: Orbit Valve provides maintenance tips and best practices to help extend the lifespan of their valves.
Contact Information:
- Phone: Available during business hours for immediate assistance.
- Email: Support queries can be sent via email for a prompt response.
- Online Resources: Comprehensive resources, including FAQs, manuals, and instructional videos, are accessible on the Orbit Valve website.
For more detailed information, customers are encouraged to visit Orbit Valve’s official website or contact their customer service department directly.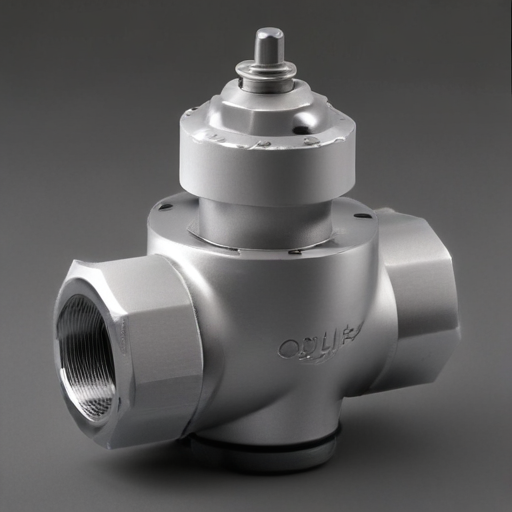
List "orbit valve" FAQ
Orbit Valve FAQ
What is an Orbit Valve?
Orbit valves are rising stem ball valves known for their unique tilt-and-turn design, which reduces seal rubbing and ensures reliable performance, even in high-temperature and critical applications. This design was first patented in 1935 and remains integral to their function today.
How do Orbit Valves work?
Orbit valves operate by tilting and turning to eliminate seal rubbing. When the valve opens, the core tilts away from the seat, allowing fluid to flow. When closing, the core turns to wedge tightly against the seat, ensuring a positive shutoff. This mechanism increases durability and reduces the risk of leakage.
Where are Orbit Valves used?
Orbit valves are widely used in the oil and gas industry, water treatment, and other industrial applications requiring precise flow control and durability under harsh conditions.
What are the benefits of using Orbit Valves?
- Reduced Seal Rubbing: Enhances the valve's lifespan and reliability.
- High Integrity: Ensures secure shutoff, reducing the risk of leaks.
- Versatility: Suitable for various high-temperature and critical isolation applications.
- Low Emissions: Some models are Low-E certified, meeting strict emission standards.
How often should Orbit Valves be maintained?
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring long-term performance:
- Annual Maintenance: At least once a year.
- Quarterly Lubrication: If the valve is operated infrequently.
- Service every 1,000 cycles: If operated frequently.
- Service every 500 cycles: In corrosive or severe service conditions.
What are common issues and solutions for Orbit Valves?
- Valve Not Closing: This can often be resolved by checking the diaphragm for debris and ensuring the solenoid is functioning correctly.
- Wear and Tear: Regular lubrication and timely servicing can prevent significant wear and tear.
How much do Orbit Valves cost?
Prices vary depending on size and application, but generally, Orbit ball valves cost between $10 and $25 per unit. Larger industrial valves used in oil and gas can be more expensive.
For more detailed information, you can visit [Orbit Valves](https://orbitvalves.com).
Top 10 FAQ with answer about orbit valve for Buyer Sourcing from China
Top 10 FAQs about Sourcing Orbit Valves from China
1. What is an orbit valve?
An orbit valve, also known as a rotating valve, is used in pipelines to control the flow of liquids or gases. It features a unique cam and lever design, minimizing wear and providing a tight seal.
2. Why source orbit valves from China?
China offers competitive pricing, a wide range of manufacturers, and advanced manufacturing capabilities. Chinese suppliers can meet various quality standards and offer customized solutions.
3. How to verify the quality of orbit valves from China?
Request certifications such as ISO, API, and CE from the supplier. Additionally, ask for sample testing, third-party inspection reports, and customer references to ensure quality compliance.
4. What are the key specifications to consider?
Key specifications include valve size, pressure rating, material composition (e.g., stainless steel, carbon steel), temperature range, and compliance with industry standards.
5. How to find reliable suppliers?
Use reputable B2B platforms like Alibaba, Made-in-China, and Global Sources. Check supplier ratings, reviews, and trade assurance programs. Attend trade shows and exhibitions for direct interactions.
6. What is the typical lead time for orbit valve orders?
Lead times vary based on order size and customization. Generally, standard orders take 30-45 days, while customized orders may take longer. Confirm with the supplier during negotiations.
7. What are the payment terms?
Common payment terms include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and D/P (Documents against Payment). Negotiate favorable terms to mitigate financial risks.
8. Are there minimum order quantities (MOQ)?
Yes, most suppliers have MOQs, which can range from a few units to several hundred, depending on the supplier. Discuss and negotiate MOQs according to your needs.
9. What about shipping and logistics?
Suppliers typically offer FOB (Free On Board) terms. Work with a reliable freight forwarder to manage shipping, customs clearance, and delivery. Understand Incoterms to avoid hidden costs.
10. How to handle after-sales service and warranties?
Ensure the supplier provides a clear warranty policy, covering manufacturing defects and offering reasonable after-sales support. Clarify the process for handling returns, replacements, or repairs.
By addressing these FAQs, buyers can effectively navigate sourcing orbit valves from China, ensuring quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.





